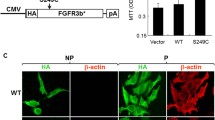
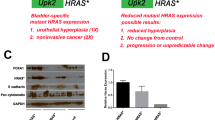
Summary
Given a role for the deregulation of p21 WAF1 in the progression of bladder tumors, we examined the growth of cultured urothelial cells from wild-type and p21WAF1 null bladders. Bladders were excised, minced from euthanized p21 WAF1 and wild-type mice, treated overnight with dispase, and then placed into flasks coated with collagen type I in Dulbecco modified Eagle medium with 10% fetal calf serum. After an overnight incubation, the media was replaced with a serumfree media and a portion of explants were treated with 12-O-tetrade-canoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) on day 7 and continued for either 4 or 9 wk. The urothelial origin of any surviving epithelial cells was determined by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) using uroplakin II-specific primers, and the expression of the cell cycle-related proteins, p16INK4 and p19ARF, was examined by semiquantitative RT-PCR and Western blotting. Isolated wild-type and serially passaged p21WAF1 null epithelial-like cells were then injected subcutaneously into nude mice. We found that phorbol ester treatment at two different concentrations significantly significantly enhanced uroepithelial colony formation from isolated wild-type mouse bladder tissue. On the other hand, significantly fewer urothelial colonies were derived from p21WAF1 null bladder cells treated with phorbol ester. Although there was apparent senescence and cell death of epithelial foci and stromal cells in phorbol ester-treated and-untreated p21WAF1 null cultures, after 3 mo there was an apparent subpopulation of epitheloid cells that overgrew each flask. There was a significant decrease in the number of these serially passaged cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle when compared with initial explant wild-type or p21 WAF1 null cells. This subpopulation of epitheloid cells expressed the mouse uroplakin II gene, indicating a urothelial phenotype, but did also a high level of expression of the p53 protein and a significant decrease in the expression of the p19ARF transcript in both p21WAF1 null bladder and p21WAF1 null cells. These p21WAF1 null cells could be easily passaged and when injected subcutaneously into nude mice, large tumors developed. Therefore, it appears that a subpopulation of urothelial cells from the p21WAF1 null bladder can develop a tumorigenic phenotype in vitro.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adnane, J.; Jackson, R. J.; Nicosia, S. V.; Cantor, A. B.; Pledger, W. J.; Sebti, S. M. Loss of p21 WAF1/CIP1 accelerates Ras oncogenesis in a transgenic/knockout mammary cancer. Oncogene 19:5338–5347; 2000.
Besson, A.; Yong, V. W. Involvement of p21 (Wafl/Cip1) in protein kinase C alpha-induced cell cycle progression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:4580–4590; 2000.
Chang, B.-D.; Watanabe, K.; Broude, E. V.; Fang, J.; Poole, J. C.; Kalinichenko, T. V.; Roninson, I. B. Effects of p21Wafl/Cip1/Sdi1 on cellular gene expression: implications for carcinogenesis, senescence, and age-related diseases. Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:4291–4296; 2000.
Deng, C.; Zhang, P.; Harper, J. W.; Elledge, S. J.; Leder, P. Mice lacking p21CIP1/WAF1 undergo normal development, but defective in G1 checkpoint control. Cell 82:675–684; 1995.
el-Deiry, W. S.; Harper, J. W.; O’Connor, P. M., et al. WAF1/CIP1 is induced in p53-mediated G1 arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 54:1169–1174; 1994.
el-Deiry, W. S.; Tokino, T.; Velculescu, V. E., et al WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell 75:817–825; 1993.
Frey, M. R.; Clark, J. A.; Leontieva, O.; Uronis, J. M.; Black, A. R.; Black, J. D. Protein kinase C signaling mediates a program of cell cycle withdrawal in the intestinal epithelium. J. Cell Biol. 151:763–778; 2000.
Groth, A.; Weber, J. D.; Willumson, B. H.; Sherr, C. J.; Roussel, M. F. Oncogenic ras induces p19ARF and growth arrest in mouse embryo fibroblasts lacking p21Cip1 and p27Kip2 without activating cyclin D-dependent kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 275:27473–27480; 2000.
Hollander, M. C.; Sheikh, M. S.; Bulavin, D. V., et al. Genomic instability in Gadd45a-deficient mice. Nat. Genet. 23:176–184; 1999.
Jung, J. M.; Bruner, J. M.; Ruan, S.; Langford, L. A.; Kyritsis, A. P.; Kobayashi, T.; Levin, V. A.; Zhang, W. Increased levels of p21 WAF1/Cip1 in human brain tumors. Oncogene 11:2021–2028; 1995.
Kawasaki, T.; Tomita, Y.; Bilim, V.; Takeda, M.; Takahashi, K.; Kumanishi, T. Abrogation of apoptosis induced by DNA-damaging agents in human bladder-cancer cell lines with p21/WAF1/CIP1 and/or p53 gene alterations. Int. J. Cancer 68(4):501–505; 1996.
Knowles, M. A.; Jani, H. Multistage transformation of cultured rat urothelium: the effect of N-methyl-N-nitrosourea, sodium saccharin, sodium cyclamate and 12-O-tetracanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Carcinogenesis 7:2059–2065; 1986.
Malkowicz, S. B.; Tomaszewski, J. E.; Linnenbach, A. J.; Cangiano, T. A.; Maruta, Y.; McGarvey, T. W. Novel p21WAF1/CIP1 mutations in superficial and invasive transitional cell carcinomas. Oncogene 13:1831–1837; 1996.
McDonald, E. R., III; Wu, G. S.; Waldman, T.; El-Deiry, W. S. Repair defect in p21WAF1/CIP1-/-human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 56:2250–2255; 1996.
McDoniels-Silvers, A. L.; Herzog, C. R.; Tyson, F. L.; Malkinson, A. M.; You, M. Inactivation of both Rb and p53 pathways in mouse lung epithelial cell lines. Exp. Lung Res. 27:297–318; 2001.
Missero, C.; Di Cunto, F.; Kiyokawa, H.; Koff, A.; Dotto, G. P. The absence of p21Cip1/WAF1 alters keratinocyte growth and differentiation and promotes ras-tumor progression. Genes Dev. 10:3065–3075; 1996.
Pantoja, C.; Serrano, M. Murine fibroblasts lacking p21 undergo senescence and are resistant to transformation by oncogenic. Ras. Oncogene 18:4974–4782; 1999.
Stein, J. P.; Ginsberg, D. A.; Grossfeld, G. D. Effect of p21WAF1/CIP1 expression on tumor progression in bladder cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 90:1072–1079; 1998.
Tadoro, G. J.; Green, H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J. Cell Biol. 17:299–313; 1963.
Topley, G. I.; Okuyama, R.; Gonzales, J. G.; Conti, C.; Dotto, P. G. p21 WAF1/CIP1 functions as a suppressor of malignant skin tumor formation and a determinant of keratinocyte stem-cell potential. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:9089–9094; 1999.
Vindelov, L. L.; Christensen, I. J. A review of techniques and results obtained in one laboratory by an integrated system of methods designed for routine clinical flow cytometric DNA analysis. Cytometry 11:753–770; 1990.
Weinberg, W. C.; Montano, N. E.; Deng, C. Loss of p21CIP1/WAF1 does not recapitulate accelerated malignant conversion caused by p53 loss in experimental skin carcinogenesis. Oncogene 15:685–690; 1997.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McGarvey, T.W., Nguyen, T.B., Tomaszewski, J.E. et al. The isolation of an immortalized and tumorigenic cell line from p21 WAF1 null mouse bladders. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 38, 394–400 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1290/1071-2690(2002)038<0394:TIOAIA>2.0.CO;2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1290/1071-2690(2002)038<0394:TIOAIA>2.0.CO;2